前阵子遇到这样一个题目,要求设计一个分布式GPU任务调度系统,需求归纳起来有几点:
- 支持任务启动、终止等常见操作;
- 支持优先级配置,资源不足的情况下尽可能满足高优先级用户的需求;
- 尽量提高系统的资源利用率;
- 保证任务可以运行到指定型号的显卡上;
- 利用k8s的任务调度机制扩展实现。
这算是我第一次思考如何解决一个应用侧的分布式问题,提出的解决方案多有不成熟,但迈出第一步还是很有成就感~
常见操作实现
按我理解每个用户请求都对应一个GPUTask的概念, 因此可以使用k8s的自定义资源(Custom Defined Resource,CDR)功能为集群拓展API,模板文件大概如下:
yaml
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: gputasks.falldio.com
spec:
group: falldio.com
names:
kind: GPUTask
plural: gputasks
singular: gputask
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1
served: true
storage: true
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
type: object
properties:
spec:
type: object
properties:
memory:
type: string
cpu:
type: string
gpu:
type: string
gpu-amount:
type: string
priority:
type: string这是一个资源模板,主要属性包括:
memory:计算任务的内存需求;cpu:任务的CPU核数需求;gpu:任务指定的显卡型号;gpu-amount:任务需要的显卡数量;priority:任务的优先级配置。
kubectl apply -f即可注册资源到集群,然后可以创建具体的GPUTask实例,如:
yaml
apiversion: falldio.com/v1
kind: gputask
metadata:
name: rtx4090
spec:
memory: 16gi
cpu: '8'
gpu: rtx4090
gpu-amount: '1'
priority: gpu-low-priority任务的启动和终止操作即可映射为对集群中的GPUTask资源的创建和删除操作,需要的话还可以进一步给资源增加uid,再用go-client把这些常见功能封起来,使用自定义控制器动态生成和删除对应的Pod。
优先级配置
优先级配置主要通过Pod的PriorityClass机制实现,当出现Pod无法被调度的情况时,k8s的调度程序会尝试抢占较低优先级的Pod,以满足悬决Pod的调度需求。
yaml
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1
kind: PriorityClass
metadata:
name: gpu-low-priority
value: 1
globalDefault: false
description: "低优先级GPU任务。"
---
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1
kind: PriorityClass
metadata:
name: gpu-medium-priority
value: 10
globalDefault: false
description: "中等优先级GPU任务。"
---
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1
kind: PriorityClass
metadata:
name: gpu-high-priority
value: 100
globalDefault: false
description: "高优先级GPU任务。"这里我们同样定义三种简单的优先级,value对应k8s中的优先等级。 而上一节的CDR中已经配置了对应的优先级内容。
Scheduler Score Plugin
为了提高资源利用率,我们需要了解k8s的调度框架。 简单地说,可以在如下时机对调度框架进行扩展:
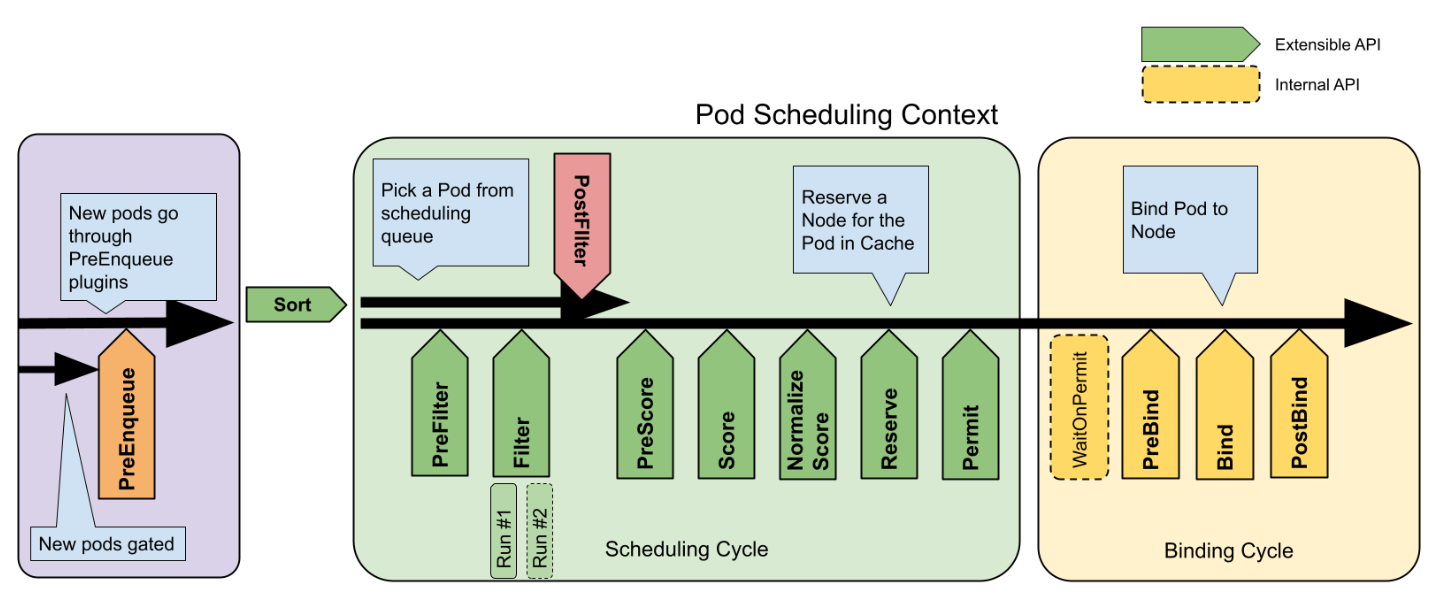
- PreEnqueue:
Pod进入调度队列之前; - Sort:对调度队列中的
Pod排序; - PreFilter:在对集群节点进行过滤之前;
- Filter:这一阶段检查节点的有效性,只有满足某些条件的节点才能被用于配置
Pod,比如本问题中特定的显卡型号; - PostFilter:过滤之后如果没有满足要求的节点,则进入该阶段;
- PreScore:在下一阶段之前记录节点状态;
- Score:按照一定规则对节点进行打分,
Pod后面会被分配到得分最高的节点上; - NormalizeScore:对得分进行微调,使其分布在特定区间;
- Reserve:锁定选择的节点,避免竟态条件;
- Permit:最终允许
Pod被调度到指定节点上。
我们要做的是自定义打分插件,实现在Score和NormalizeScore阶段的自定义。
- clone scheduler-plugins项目;
- 在pkg目录下创建自定义插件目录,实现
framework.ScorePlugin接口。
对于Score,我们主要根据节点CPU、内存和显卡数量的余量进行打分:
go
func (gs *GPUScore) Score(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
nodeInfo, err := gs.handle.SnapshotSharedLister().NodeInfos().Get(nodeName)
if err != nil {
return 0, framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, fmt.Sprintf("getting node %q from Snapshot: %v", nodeName, err))
}
return gs.score(pod, nodeInfo)
}
func (gs *GPUScore) score(pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) (int64, *framework.Status) {
node := nodeInfo.Node()
if node == nil {
return 0, framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, "node not found")
}
if nodeInfo.Allocatable == nil {
return 0, framework.NewStatus(framework.Error, "allocatable resources not found")
}
cpuScore := gs.calculateResourceScore(v1.ResourceCPU, pod, nodeInfo)
memScore := gs.calculateResourceScore(v1.ResourceMemory, pod, nodeInfo)
score := cpuScore + memScore
return score, nil
}
func (gs *GPUScore) calculateResourceScore(resource v1.ResourceName, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) int64 {
podRequest := calculatePodResourceRequest(pod, resource)
var allocatable int64
switch resource {
case v1.ResourceCPU:
allocatable = nodeInfo.Allocatable.MilliCPU
case v1.ResourceMemory:
allocatable = nodeInfo.Allocatable.Memory
case "falldio.com/gpu":
allocatable = nodeInfo.Allocatable.ScalarResources["falldio.com/gpu"]
}
return allocatable - podRequest
}至于NomalizeScore则更简单,我们使用常见的归一化公式即可:
go
func (gs *GPUScore) NormalizeScore(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, p *v1.Pod, scores framework.NodeScoreList) *framework.Status {
var max int64 = math.MinInt64
var min int64 = math.MaxInt64
for _, score := range scores {
if score.Score > max {
max = score.Score
}
if score.Score < min {
min = score.Score
}
}
oldRange := max - min
newRange := framework.MaxNodeScore - framework.MinNodeScore
for i, score := range scores {
if oldRange == 0 {
scores[i].Score = framework.MinNodeScore
} else {
scores[i].Score = ((score.Score - min) * newRange / oldRange) + framework.MinNodeScore
}
}
return nil
}通过nodeSelector指定显卡
实现指定显卡功能的最简单的方法是给集群节点打label,然后在Pod的nodeSelector字段指示显卡型号信息。在go-client中即按如下方式声明Pod:
go
newPod := &v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: gpuTask.Name,
Namespace: gpuTask.Namespace,
Labels: map[string]string{"app": "gpu-task"},
},
Spec: v1.PodSpec{
NodeSelector: map[string]string{
"falldio.com/gpu": gpuTask.Spec.GPU,
},
Containers: []v1.Container{
{
Name: "gpu-task",
Image: "nvidia/cuda:11.0-base",
Resources: v1.ResourceRequirements{
Limits: v1.ResourceList{
v1.ResourceCPU: resource.MustParse(gpuTask.Spec.CPU),
v1.ResourceMemory: resource.MustParse(gpuTask.Spec.Memory),
"falldio.com/gpu": resource.MustParse(gpuTask.Spec.GPUAmount),
},
},
},
},
PriorityClassName: string(gpuTask.Spec.Priority),
},
}